
- Diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the pancreas can no longer make insulin, or the body cannot effectively use insulin.
- Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that acts like a key to let glucose from the food we eat pass from the bloodstream into the cells in the body to produce energy. The body breaks down all carbohydrate foods into glucose in the blood, and insulin helps glucose move into the cells.
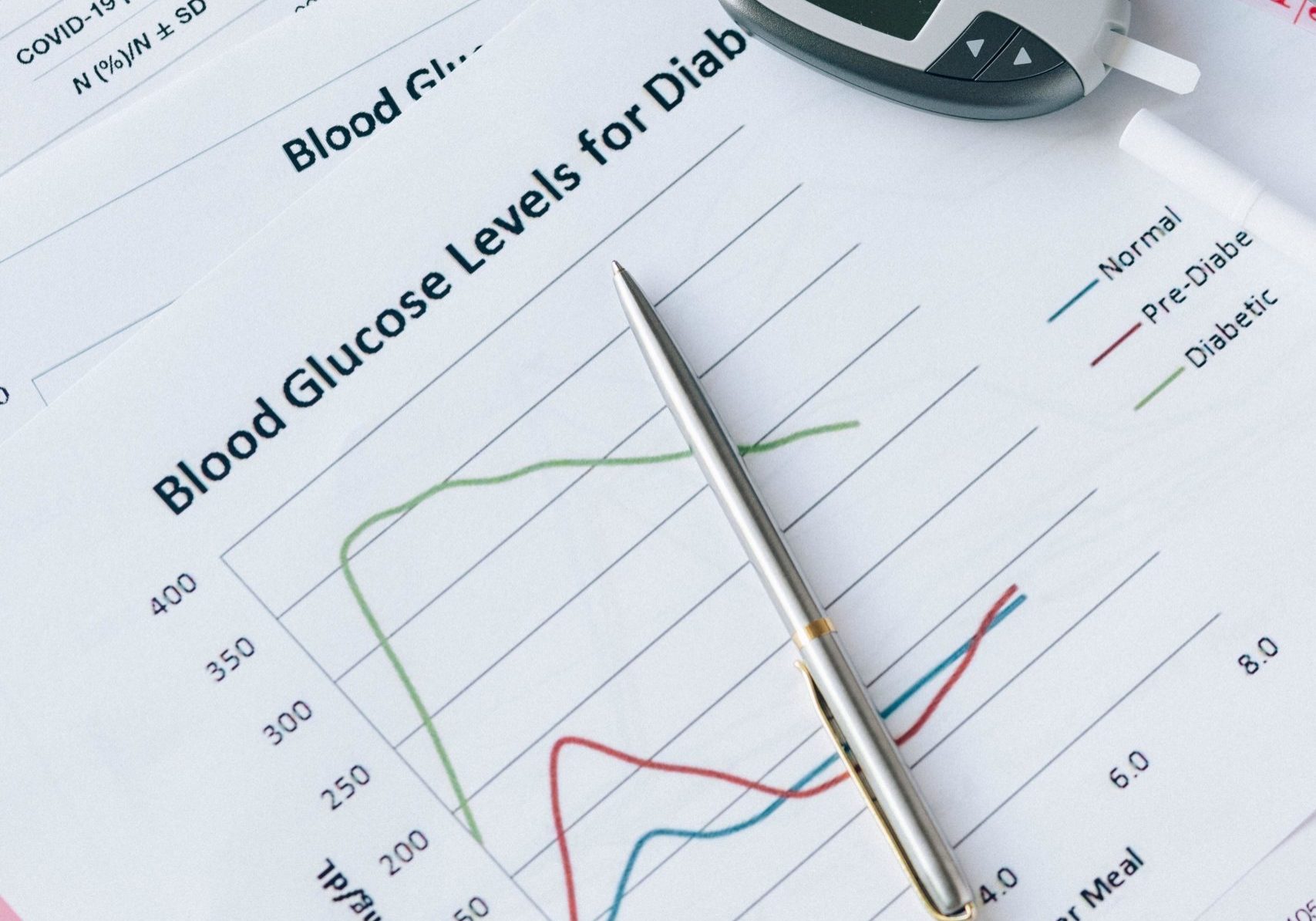
- When the body cannot produce or use insulin effectively, this leads to high blood glucose levels, called hyperglycaemia. Over the long-term high glucose levels are associated with damage to the body and failure of various organs and tissues.
most common types of diabetes

Type 1
Type 1 diabetes was once called juvenile diabetes, but it can develop at any age and requires insulin treatment for survival. Only about 5-10% of people with diabetes have Type 1. According to the CDC, Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). This reaction destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin.
Some people have certain genes that make them more likely to develop Type 1 diabetes, but many of them won’t go on to develop it. A trigger in the environment, such as a virus, may also play a part in developing Type 1 diabetes. Diet and lifestyle habits don’t cause Type 1 diabetes.

Type 2
Type 2 diabetes accounts for around 90% of all diabetes and is more commonly diagnosed in adults. The pancreas does not produce enough insulin and/or the body doesn't use it efficiently.
Type 2 diabetes used to be known as adult-onset diabetes, but both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can begin during childhood and adulthood. The increase in the number of children with obesity has led to more cases of Type 2 diabetes in younger people.

Pre-Diabetes
Prediabetes means you have a higher than normal blood sugar level. It's not high enough to be considered Type 2 diabetes yet, but without lifestyle changes, adults and children with pre-diabetes are at high risk to develop Type 2 diabetes.
Engaging in physical activity as part of your daily routine, eating healthier foods, and staying at a healthy weight can help bring your blood sugar level back to normal. The same lifestyle changes that can help prevent Type 2 diabetes in adults might also help bring children's blood sugar levels back to normal.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes is a type of diabetes that can develop during pregnancy in women who don't already have diabetes. Every year, 2% to 10% of pregnancies in the United States are affected by gestational diabetes. Effectively managing gestational diabetes will increase the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.

Symptoms of diabetes can include:
- Increased thirst.
- Frequent urination.
- Increased hunger.
- Unintended weight loss.
- Fatigue.
- Blurred vision.
- Slow-healing sores.
- Frequent infections.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet.
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck.
If you notice any symptoms of diabetes, please seek a healthcare provider. For additional information on diabetes, please visit the CDC website.
diabetes in underserved communities

Income Disparities
Diabetes impacts all social, economic, and ethnic backgrounds but effects people in low to middle income areas at a greater rate (lack of access to medical care, healthy food options, lack of education, etc.)
“We found that low-income populations are more likely to have diabetes and that income-related inequalities in diabetes appear to have widened over the past decade,” said Yu Chen, Ph.D. (ADA, 2023)

Racial Disparities
American Indians and Pacific Islanders have the highest rates of diabetes among the 5 racial groups counted in the U.S. Census. They’re more than twice as likely to have the condition as whites, who have about an 8% chance of having it as adults.
Diabetes is also more common among African-Americans and Asian Americans compared to whites. Hispanics living in the U.S. are 17% more likely to have Type 2 diabetes than non-Hispanic white people.

